Dart Cheat Sheet and Quick Reference
Source: raywenderlich.com
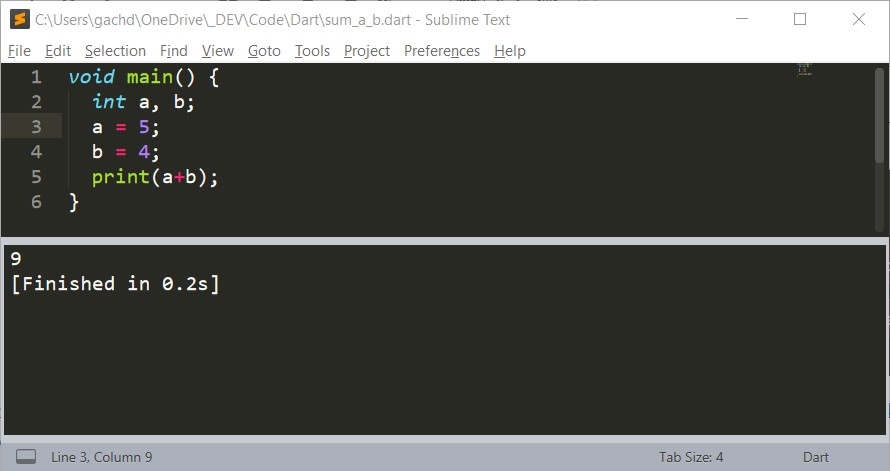
main() function
void main() {
print('Hello, Dart!');
}
Variables, Data Types, & Comments
// Use var with type inference or instead use type name directly
var myAge = 35; // inferred int created with var
var pi = 3.14; // inferred double created with var
int yourAge = 27; // type name instead of var
double e = 2.718; // type name instead of var
// This is a comment
print(myAge); // This is also a comment.
/*
And so is this.
*/
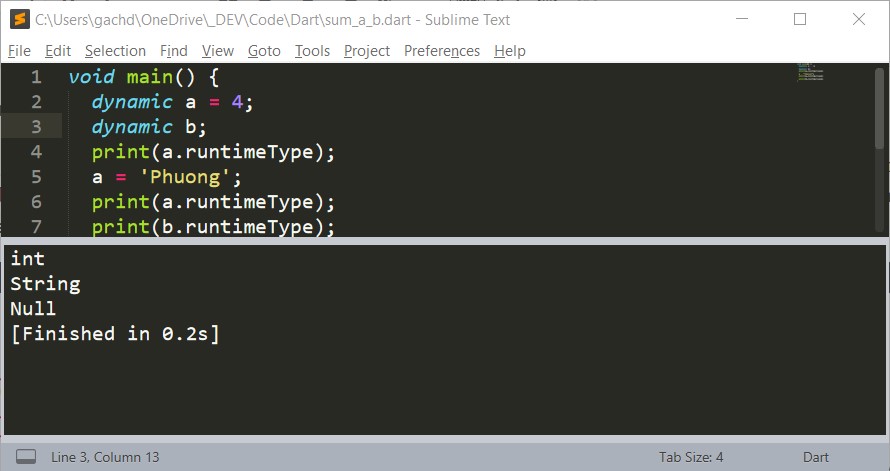
// dynamic can have value of any type
dynamic numberOfKittens;
// dynamic String
numberOfKittens = 'There are no kittens!';
numberOfKittens = 0; // dynamic int
numberOfKittens = 1.0; // dynamic double
bool areThereKittens = true; // bool
// Compile-time constants
const speedOfLight = 299792458;
// Immutables with final
final planet = 'Jupiter';
// planet = 'Mars'; // error: planet is immutable
// Enumerations
enum Month { january, february, march, april, may, june, july, august, september, october, november, december }
final month = Month.august;
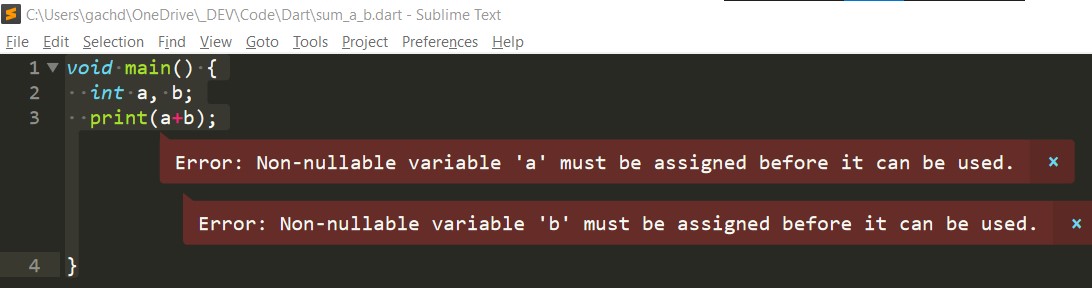
Null
int age; // initialized to null
double height;
String err;
// Check for null
var error = err ?? "No error"; // No error
// Null-check compound assignment
err ??= error;
// Null-check on property access
print(age?.isEven);
Operators
// Arithmetic
40 + 2; // 42
44 - 2; // 42
21 * 2; // 42
84 / 2; // 42
84.5 ~/ 2.0; // int value 42
392 % 50; // 42
// Types can be implicitly converted
var answer = 84.0 / 2; // int 2 to double
// Equality and Inequality
42 == 43; // false
42 != 43; // true
// Increment and decrement
print(answer++); // 42, since it prints first for postfix
print(--answer); // 42, since it decrements first for prefix
// Comparison
42 < 43; // true
42 > 43; // false
42 <= 43; // true
42 >= 43; // false
// Compound assignment
answer += 1; // 43
answer -= 1; // 42
answer *= 2; // 84
answer /= 2; // 42
// Logical
(41 < answer) && (answer < 43); // true
(41 < answer) || (answer > 43); // true
!(41 < answer)); // false
Strings
// Can use single or double quotes for String type
var firstName = 'Albert';
String lastName = "Einstein";
// Escape sequences such as \' and \n
// and concatenating adjacent strings
var quote = 'If you can\'t' ' explain it simply\n'
"you don't understand it well enough.";
// Concatenation with +
var energy = "Mass" + " times " + "c squared";
// Preserving formatting with """
var model = """
I'm not creating the universe.
I'm creating a model of the universe,
which may or may not be true.""";
// Raw string with r prefix
var rawString =r”I'll\nbe\nback!"; // prints I’ll\nbe\nback!
Control Flow: Conditionals
var animal = 'fox';
if (animal == 'cat' || animal == 'dog') {
print('Animal is a house pet.');
} else if (animal == 'rhino') {
print('That\'s a big animal.');
} else {
print('Animal is NOT a house pet.');
}
// switch statement
enum Semester { fall, spring, summer }
Semester semester;
switch (month) {
case Month.august:
case Month.september:
case Month.october:
case Month.november:
case Month.december:
semester = Semester.fall;
break;
case Month.january:
case Month.february:
case Month.march:
case Month.april:
case Month.may:
semester = Semester.spring;
break;
case Month.june:
case Month.july:
semester = Semester.summer;
break;
}
Control Flow: While loops
var i = 1;
// while, print 1 to 9
while (i < 10) {
print(i);
i++;
}
// do while, print 1 to 9
i = 1;
do {
print(i);
++i;
}
while (i < 10);
// break at 5
do {
print(i);
if (i == 5) {
break;
}
++i;
} while (i < 10);
Control Flow: For loops
var sum = 0;
// Init; condition; action for loop
for (var i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
sum += i;
}
// for-in loop for list
var numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4];
for (var number in numbers) {
print(number);
}
// Skip over 3 with continue
for (var number in numbers) {
if (number == 3) {
continue;
}
print(number);
}
// forEach with function argument
numbers.forEach(print); // 1, 2, 3, 4 on separate lines
// forEach with anonymous function argument
numbers = [13, 14, 15, 16];
numbers.forEach((number) => print(number.toRadixString(16)); // d, e, f, 10
Functions
// Named function
bool isBanana(String fruit) {
return fruit == 'banana';
}
var fruit = 'apple';
isBanana(fruit); // false
// Optional parameters with square brackets
String fullName(String first, String last, [String title]) {
return "${title == null ? "" : "$title "}$first
$last";
}
fullName("Ray", "Wenderlich"); // Ray Wenderlich
fullName("Albert", "Einstein", "Professor"); //Professor Albert Einstein
// Optional named arguments with braces
bool withinTolerance(int value, {int min, int max}) {
return (min ?? 0) <= value && value <= (max ??
10);
}
withinTolerance(11, max: 10, min: 1); // false
// Default values
bool withinTolerance(int value, {int min = 0, int max = 10}) {
return min <= value && value <= max;
}
withinTolerance(5); // true
// Function as parameter
int applyTo(int value, int Function(int) op) {
return op(value);
}
int square(int n) {
return n * n;
}
applyTo(3, square); // 9
// Arrow syntax for one line functions
int multiply(int a, int b) => a * b;
multiply(14, 3); // 42
Anonymous Functions and Closures
// Anonymous functions (without a name)
// Assign anonymous function to a variable
var multiply = (int a, int b) {
return a * b;
}
// Call a function variable
multiply(14, 3); // 42
// Closures
Function applyMultiplier(num multiplier){
// Return value has access to multiplier
return (num value) => value * multiplier;
}
var triple = applyMultiplier(3);
triple(14.0); // 42.0
Collections: Lists
// Fixed-size list
var pastries = List<String>(3);
// Element access by index
pastries[0] = 'cookies';
pastries[1] = 'cupcakes';
pastries[2] = 'donuts';
// Growable list
List<String> desserts = [];
desserts.add('cookies');
// Initialize by growable list
var desserts = ['cookies', 'cupcakes', 'pie'];
// List properties and methods
desserts.length; // 3
desserts.first; // 'cookies'
desserts.last; // 'pie'
desserts.isEmpty; // false
desserts.isNotEmpty; // true
desserts.firstWhere((str) => str.length < 4));// pie
// Collection if
var peanutAllergy = true;
var candy = ['junior mints', 'twizzlers', if (!peanutAllergy) 'reeses'];
// Collection for
var numbers = [1, 2, 3];
var doubledNumbers = [for (var number in numbers) 2 * number]; // [2, 4, 6]
Collections: List Operations
// Spread Operator and null-spread operator
var pastries = ['cookies', 'cupcakes'];
var desserts = ['donuts', ...pastries, ...?candy];
// Map to transform list
var numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4];
var squares = numbers.map((number) => number * number).toList(); // [1, 4, 9, 16]
// Filter list using where
var evens = squares.where((square) => square.isEven); // (4, 16)
// Reduce list to combined value
var amounts = [199, 299, 299, 199, 499];
var total = amounts.reduce((value, element) => value + element); // 1495
Collections: Sets
// Create set of int
var someSet = <int>{};
// Set type inference
var anotherSet = {1, 2, 3, 1};
// Check for element
anotherSet.contains(1); // true
anotherSet.contains(99); // false
// Adding and removing elements
someSet.add(42);
someSet.add(2112);
someSet.remove(2112);
// Add to set from list
someSet.addAll([1, 2, 3, 4]);
// Intersection
var intersection = someSet.intersection(anotherSet);
// Union
var union = someSet.union(anotherSet);
Collections: Maps
// Map from String to int
var emptyMap = Map<String, int>();
// Map from String to String
var avengers = {"Iron Man": "Suit", "Captain America": "Shield", "Thor": "Hammer"};
// Element access by key
var ironManPower = avengers["Iron Man"]; // Suit
avengers.containsKey("Captain America"); // true
avengers.containsValue("Arrows"); // false
// Access all keys and values
avengers.keys.forEach(print); // Iron Man, Captain America, Thor
avengers.values.forEach(print); // Suit, Shield, Hammer
// Loop over key-value pairs
avengers.forEach((key, value) => print('$key -> $value'));
Classes and Objects
class Actor {
// Properties
String name;
var filmography = <String>[];
// Short-form constructor
Actor(this.name, this.filmography);
// Named constructor
Actor.rey({this.name = "Daisy Ridley"}) {
filmography = ['The Force Awakens', 'Murder on the Orient Express'];
}
// Calling other constructors
Actor.inTraining(String name) : this(name, []);
// Constructor with initializer list
Actor.gameOfThrones(String name): this.name = name, this.filmography = ['Game of Thrones'] {
print('My name is ${this.name}');
}
// Getters and Setters
String get debut => '$name debuted in ${filmography.first}';
set debut(String value) => filmography.insert(0, value);
// Methods
void signOnForSequel(String franchiseName) {
filmography.add('Upcoming $franchiseNamesequel');
}
// Override from Object
String toString() => "${[name, ...filmography].join("\n- ")}\n";
}
var gotgStar = Actor('Zoe Saldana', []);
gotgStar.name = 'Zoe Saldana';
gotgStar.filmography.add('Guardians of the Galaxy');
gotgStar.debut = 'Center Stage';
print(Actor.rey().debut); // The Force Awakens
var kit = Actor.gameOfThrones('Kit Harington');
var star = Actor.inTraining('Super Star');
// Cascade syntax ..
gotgStar // Get an object
..name = 'Zoe' // Use property
..signOnForSequel('Star Trek'); // Call method
Static Class Members
enum PhysicistType { theoretical, experimental, both
}
class Physicist {
String name;
PhysicistType type;
// Internal constructor
Physicist._internal(this.name, this.type);
// Static property
static var physicistCount = 0;
// Static method
static Physicist newPhysicist(
String name,
PhysicistType type) {
physicistCount++;
return Physicist._internal(name, type);
}
}
final emmy = Physicist.newPhysicist(
"Emmy Noether", PhysicistType.theoretical);
final lise = Physicist.newPhysicist(
"Lise Meitner", PhysicistType.experimental);
print(Physicist.physicistCount); //2
Class Inheritance
// Base aka parent class
class Person {
// Parent properties inherited by child
String firstName;
String lastName;
// Parent class constructor
Person(this.firstName, this.lastName);
// Parent class method
String get fullName => '$firstName $lastName';
// Optional @override annotation
// All class hierarchies and types have Object as root class
@override
String toString() => fullName;
}
// Subclass aka child class
class Student extends Person {
// Properties specific to child
var grades = <String>[];
// Call super on parent constructor
Student(String firstName, String lastName): super(firstName, lastName);
// Optional override annotation on parent method override
@override
String get fullName => '$lastName, $firstName';
}
final jon = Person('Jon', 'Snow');
final jane = Student('Jane', 'Snow'); // Calls parent constructor
print(jon); // Jon Snow
// Use toString in parent, in turn using subclass override of fullName
print(jane); // Snow, Jane
Abstract Classes, Interfaces, Mixins
enum BloodType { warm, cold }
abstract class Animal {
BloodType bloodType; // Base class property
void goSwimming(); // Abstract method without implementation
}
mixin Milk {
bool hasMilk;
bool doIHaveMilk() => hasMilk;
}
// Concrete class inheriting from abstract class
class Cat extends Animal with Milk {
BloodType bloodType = BloodType.warm; // Set value for property
Cat() { hasMilk = true; } // Set mixin property
// Concrete subclass must implement abstract methods
@override
void goSwimming() { print("No thanks!"); }
}
// Concrete class that also implements Comparable interface
class Dolphin extends Animal implements
Comparable<Dolphin> {
BloodType bloodType = BloodType.warm;
double length; // Concrete sublcass property
Dolphin(this.length); // Concrete subclass constructor
// Concrete subclass must implement abstract methods
@override
void goSwimming() { print("Click! Click!"); }
// Also must implement interface methods
@override
int compareTo(other) =>
length.compareTo(other.length);
@override
String toString() => '$length meters';
}
class Reptile extends Animal with Milk {
BloodType bloodType = BloodType.cold;
Reptile() { hasMilk = false; }
@override
void goSwimming() { print("Sure!"); }
}
// var snake = Animal(); // error: can't instantiate abstract class
// Can instantiate concrete classes
var garfield = Cat();
var flipper = Dolphin(4.0);
var snake = Reptile();
// Call concrete methods
flipper.goSwimming(); // Click! Click!
garfield.goSwimming(); // No thanks!
// Use interface implementation
var orca = Dolphin(8.0); var alpha = Dolphin(5.0);
var dolphins = [alpha, orca, flipper];
dolphins.sort();
print(dolphins); // [4 meters, 5 meters, 8 meters]
print(snake.doIHaveMilk()); // false
print(garfield.doIHaveMilk()); // true